Turkish phrasebook - Pronunciation guide
Turkish pronunciation looks daunting to non-native speakers, as many of the words are very long and look like tongue-twisters. With a bit of practice, however, it becomes much easier.
Vowels
The Turkish vowels are
- A - a short sound, as in the English car
- E - a short sound, as in the English pet
- I - the sound in the English hit and at the beginning of Istanbul
- I - a "neutral" sound with no real equivalent in English. The closest sound is the "uh" which replaces the "e" in the second syllable of open
- O - as in the English order
- Ö - pronounced as in German, a blend of "o" and "e"
- U - short as in the English put
- Ü - pronounced as in German, a blend of "u" and "e"
Remember that, in lower case, the two letters I and I look different as well. The lower case form of I is i, while the lower case form of I is i.
Consonants
- B - as in bed
- C - pronounced as the initial letter in the English jump
 - the "ch" sound in the English chapel
- the "ch" sound in the English chapel- D - as in drum
- F - as in far
- G - as in girl
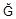 - a silent letter, which serves to lengthen the previous vowel
- a silent letter, which serves to lengthen the previous vowel- H - as in hello
- J - pronounced as in the French name Jean
- K - as in king
- L - as in love
- M - as in man
- N - as in new
- P - as in print
- R - as in run
- S - as in snake
 - the "sh" sound in the English shake
- the "sh" sound in the English shake- T - as in take
- V - roughly the mid-point between the "v" in very and the "w" in was
- Y - as in yet
- Z - as in zoo'
________
Go to top | Go to TOC | This article uses material from: -1-