Kennedy & Violich Architecture, Ltd.
Location Hamburg, Germany
Surface area 9,902 square feet
Photographs © Kennedy & Violich Architecture © Michael Moser
| Landscape
integration Good transportation and walkability |
|
| Photovoltaic
solar energy: orientable panels CO2 low consumption |
|
| Local
material: wood Recyclable materials Sustainable wood |
|
| Natural
daylighting Natural ventilation |
|
| Domotics:
Soft House smart building management system (BMS) Smart curtains |
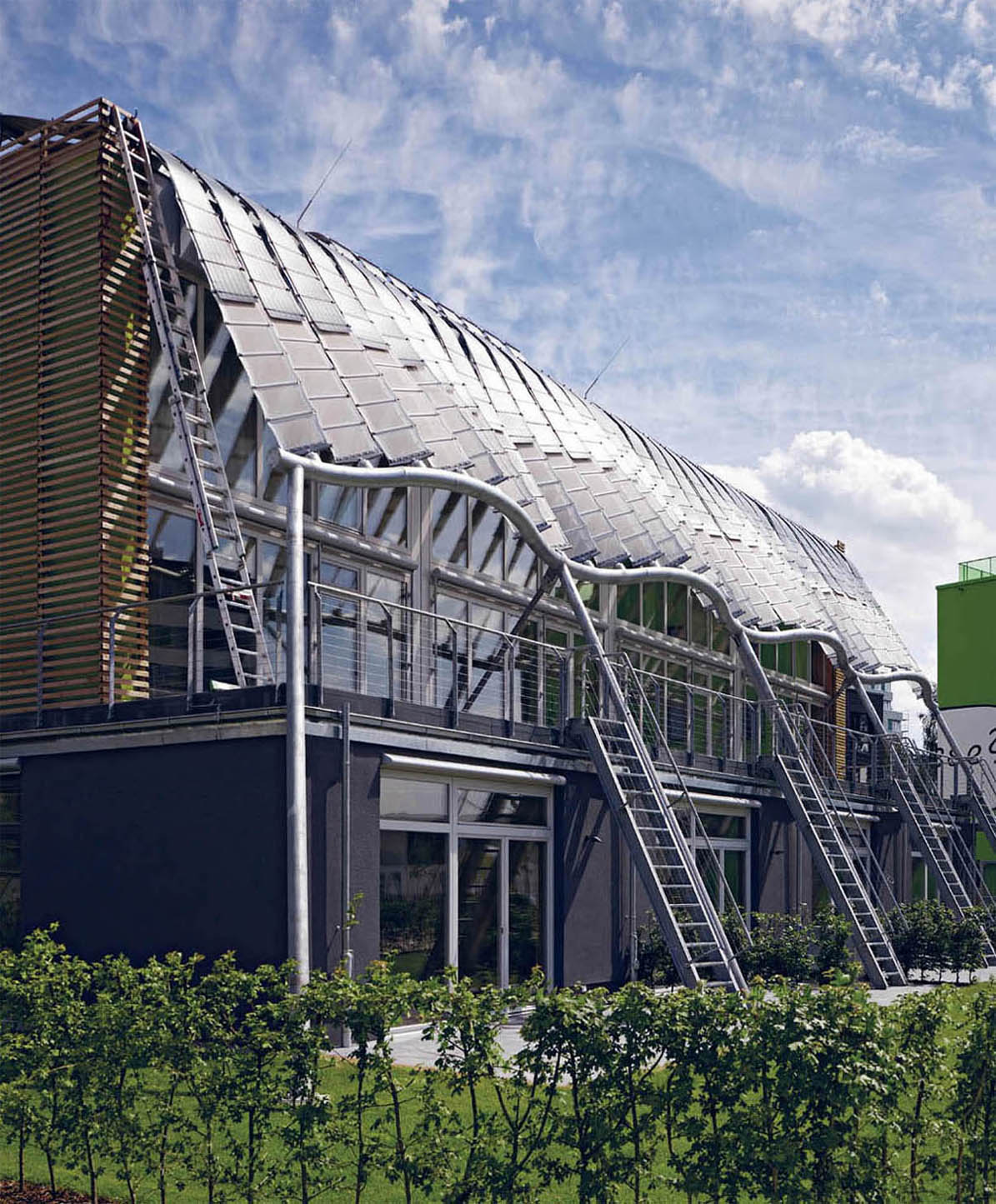
Completed in June 2013, this is a set of four housing units designed for life and work. The project’s construction gains its character from a traditional structure made of solid local wood, which can be fully recycled at the end of the building’s life span. The architectural shell is simple, solid, and durable. The organization of the design shows how a domestic infrastructure can become a “soft” attractive, ecological, solid-wood construction.
The clean domestic energy, lighting, and elements that liberate the internal spaces are transformed into a type of mobile furniture, and are interactive, upgradable, and connected to the home’s wireless network, an intelligent building management system. Thus designed for a flexible life, the wireless controls of the building articulate an infrastructure of sensitive textiles that establishes a new public identity for architecture.
This Kennedy & Violich Architecture project meets and exceeds the stringent German Passivhaus Institut environmental standards: it transforms the rigid typology that these environmental requirements impose, to create a free house with zero carbon footprint, which is adaptable and can be personalized to meet the changing needs of the owners and of the house itself.



Site plans



Upper floor

Middle floor

Ground floor

![]() The
solid wood floors and walls give the architectural structure
permanence yet are totally recyclable upon the completion of the
building’s useful life.
The
solid wood floors and walls give the architectural structure
permanence yet are totally recyclable upon the completion of the
building’s useful life.

West elevation

South elevation

East elevation

North elevation

Sections
I. Terrace entry
II. Garden entry
III. Primary entry
a. Terrace and private garden
b. Living room
c. Winter garden
d. Mechanical room
e. Bathroom / Laundry
f. Upper terrace / Garden
g. Bridge
h. Stairwell with wire mesh
i. Bedroom
j. Skylight with reflectus
k. Kitchen
l. Garage
1. Geothermal pump
2. Hotwater tank
3. Radiant cooling and heating
4. Mechanical ventilation return
5. Mechanical ventilation supply
6. Views to park and canal
7. Winter position
8. Fall position
9. Summer position
10. Hurricane position
11. Electrical distribution panel (AC)
12. AC-DC converter
13. DC mechanical device
14. AC mechanical device
15. AC receptable
16. DC 30v. lighting
17. DC motors
18. DC system controller and wireless dimmer
19. Photovoltaic cell
20. Stacking effect for natural ventilation
21. Views to sky and dynamic membrane

![]() Like
a sunflower, the facade moves to capture the maximum amount of
solar energy. The flexible and innovative photovoltaic structure
surrounding one side of the building adapts every day to the sun’s
movement.
Like
a sunflower, the facade moves to capture the maximum amount of
solar energy. The flexible and innovative photovoltaic structure
surrounding one side of the building adapts every day to the sun’s
movement.

Smart building systems axon
1. Wind sensor
2. Data
3. SOFT HOUSE. Clean Energy System GNU / Linux / Mac OS / Windows / Java
4. Internet
5. Open source
6. Community: user group
7. Visual breeze
8. Fan
9. Soft ducts
10. USB

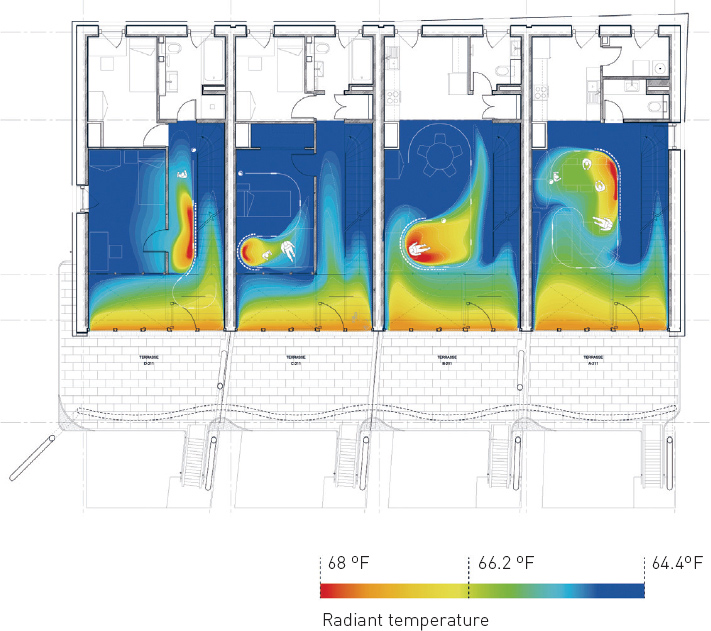
Interior thermal climate diagram


![]() The
design expands on the traditional functions of the curtain. By
allowing movement, “rooms” are instantly created that can trap
sunlight and use it to heat or cool the house.
The
design expands on the traditional functions of the curtain. By
allowing movement, “rooms” are instantly created that can trap
sunlight and use it to heat or cool the house.