Snøhetta
Location Kingston, Tasmania, Australia
Surface area 2,368 square feet
Photographs © Bruce Damonte © Snøhetta © EVE
| Landscape integration | |
| Solar
hot-water system Rainwater collection and use |
|
| Photovoltaic
solar energy CO2 low consumption Geothermal energy Passive solar / High insulation |
|
| Sustainable
wood Prefabricated materials Local materials |
|
| Natural
daylight Natural ventilation |
ZEB Pilot House is a cooperation between Snøhetta; SINTEF, the largest independent research organization in Scandinavia; the partner of ZEB; Brødrene Dahl, and Optimera. Although the project focuses on the design of a detached house, it has become a demonstration platform to facilitate learning about the methodology of construction using integrated sustainable solutions.
The design of an ambitious environmental project such as this is driven by knowledge of new technologies, local energy sources, materials and construction techniques, and other local resources, as well as the intelligent placement and orientation of the house to make optimal use of energy resources. Clearly, high environmental ambitions create new parameters in the design process.
In parallel, the project retains the comfortable qualities that are vital in any home. The need to achieve comfort and a sense of well-being dominates the design process to the same extent as its energy demands. To this end, the project boasts a variety of spaces that can be enjoyed throughout the year and includes fruit trees and vegetable gardens outside to accommodate small-scale food production.


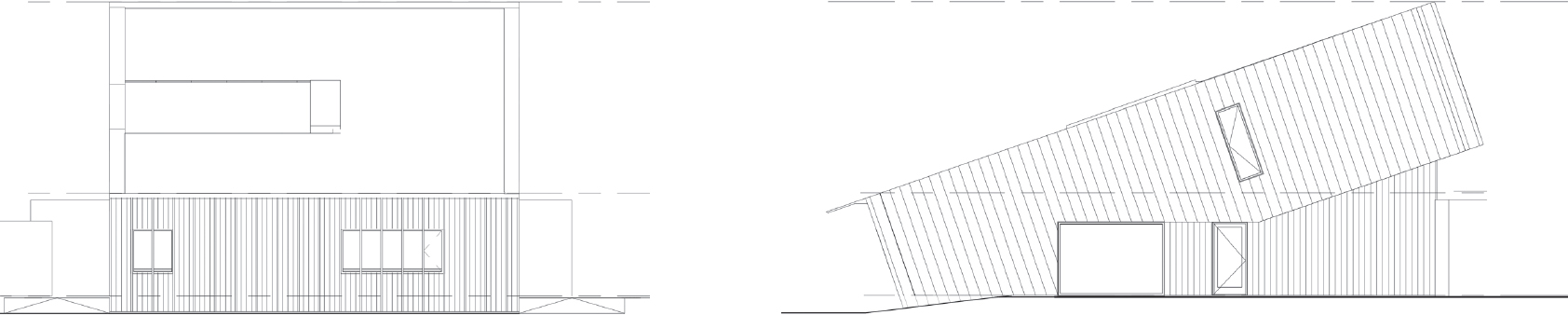

Elevations

Diagram of low energy consumption and bioclimatic strategies
1. Solar cells (photovoltaic panels) 1,600 ft2 - 19200 kWh/year
2. Solar collectors 170 ft2 - 4000 kWh/year
3. Roof slope 19
4. Rainwater collection
4a. Toilet
4b. Garden
5. Passive exterior sun shading
6. Light and air are automatically controlled based on use and need.
7. Thermal mass stabilizes the temperature.
8. The boiler gets heated water from the solar collectors, an energy well, the air system, and the water heat recovery systems.
9. Radiant floor heating heats the house.
10. Gray water heat recovery, drain water heat recovery.
11. One radiator on each floor can heat the whole house.
12. Excess heat from the indoor air is used to heat the incoming air and tap water.
13. Windows with a good U-value
14. Efficient insulation
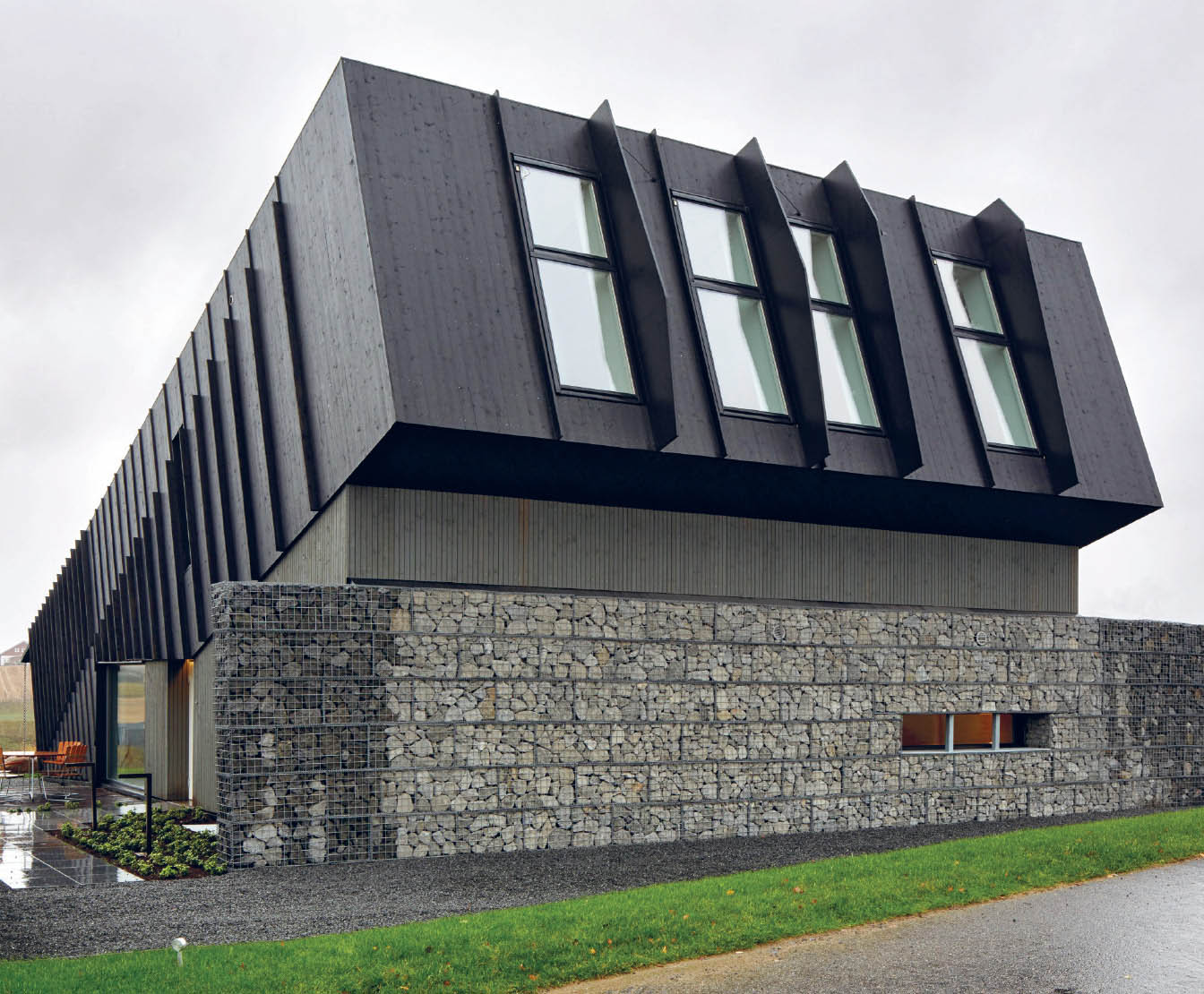


![]() The
sloped roof is festooned with solar panels, which, along with
geothermal energy, cover the house’s energy needs and generate more
than enough energy to supply an electric car all year long.
The
sloped roof is festooned with solar panels, which, along with
geothermal energy, cover the house’s energy needs and generate more
than enough energy to supply an electric car all year long.
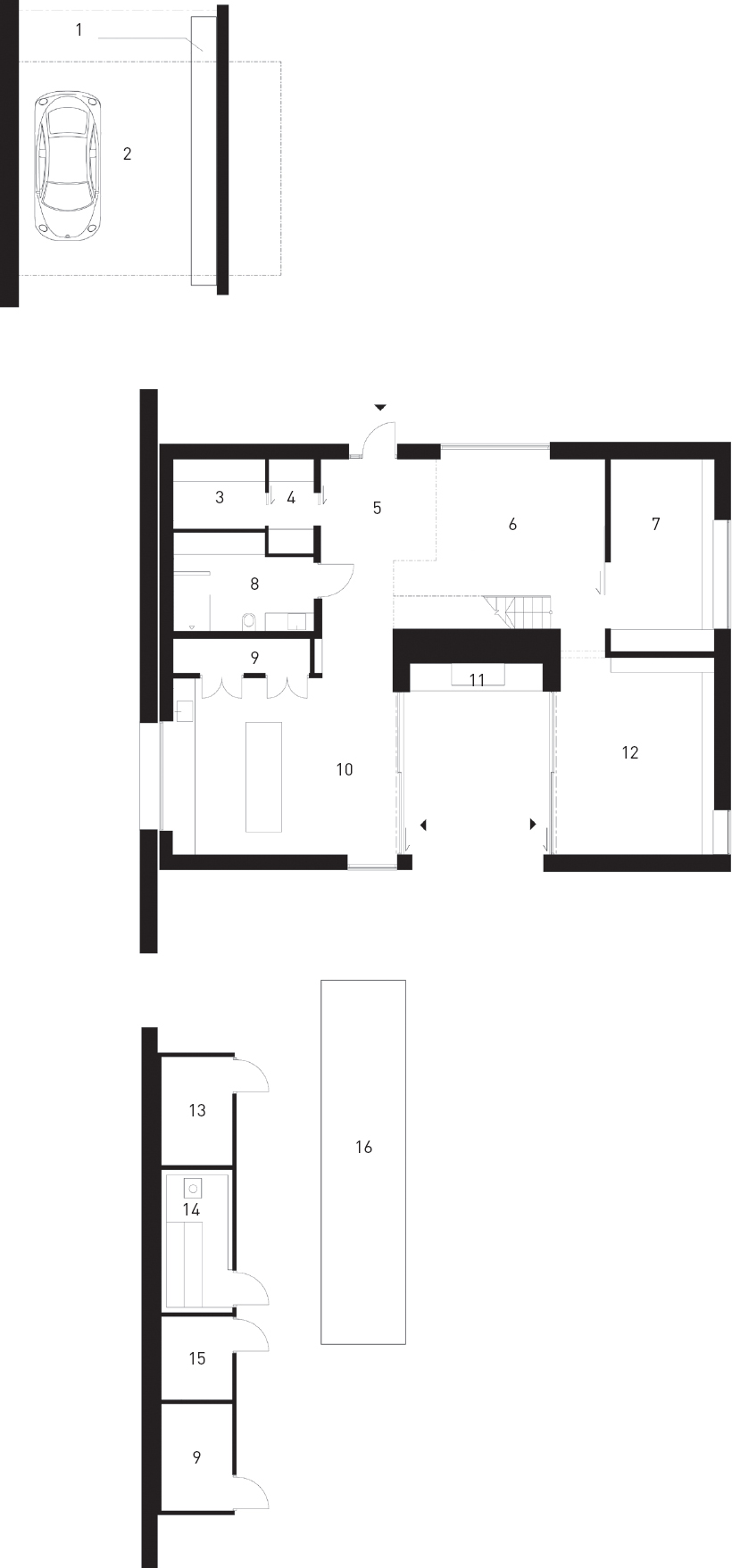
Ground floor

First floor
1. Inverters and battery bank
2. Carport / Cyclepart
3. Storeroom
4. Cloak room
5. Entrance
6. Multimedia room
7. Guest room / Office
8. Bathroom / Washroom
9. Technical room
10. Kitchen / Dining room
11. Fireplace
12. Living room
13. Garden storage
14. Sauna
15. Outside shower
16. Swimmimg pool
17. Bedrooms
18. Bathroom
19. Mezzanine
20. Void
21. Skylight
22. Cut volume

![]() From
early spring until late autumn, an open-air atrium with outdoor
furniture invites life outside the home into a beautiful space with
walls made of recycled wood and stacked bricks.
From
early spring until late autumn, an open-air atrium with outdoor
furniture invites life outside the home into a beautiful space with
walls made of recycled wood and stacked bricks.



![]() The
materials used inside were selected for their capacity to
contribute to a pleasant interior climate and air quality but
without forgetting about aesthetics.
The
materials used inside were selected for their capacity to
contribute to a pleasant interior climate and air quality but
without forgetting about aesthetics.

